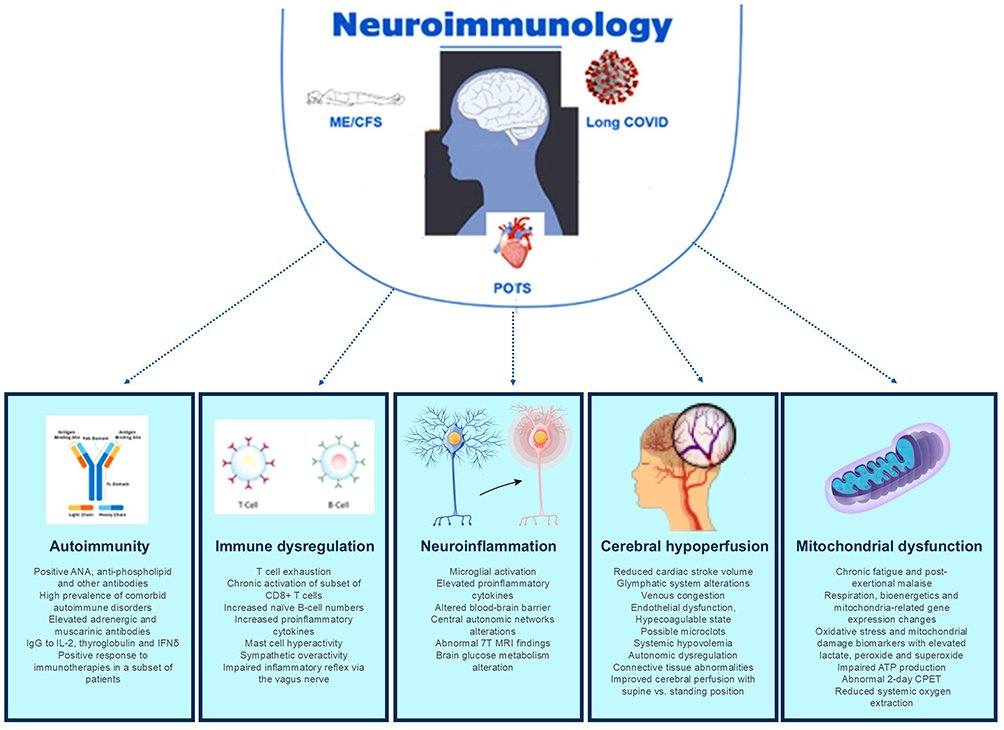
Patients recovering from COVID-19 can experience a range of long-term post-acute effects. The potential clinical and economic burden of these outcomes is unclear. This study, published by BMC Medicine in the USA in 2023, evaluated diagnoses, medications, healthcare utilisation, and medical costs before and after acute COVID-19 illness in US patients who were not at high risk of severe COVID-19.
The results showed that those who were hospitalised, with or without ICU admission, during the acute phase had the greatest increases in comorbidities and healthcare resource utilisation. However, the burden was apparent across all cohorts. The conclusion as evidenced by resource use in the post-acute phase, COVID-19 places a significant long-term clinical and economic burden among US individuals, even among patients whose acute infection did not merit hospitalisation.
You can read the study here.